Introduction
The promise of satellite connectivity for smartphones has been a tantalizing one, offering the potential to stay connected even in the most remote areas. While Apple has taken the lead with its iPhone 14, Android users are still waiting for their chance to experience this transformative technology.
The Qualcomm-Iridium Partnership and Its Demise
In early 2023, Qualcomm, the leading chipmaker for Android devices, unveiled Snapdragon Satellite, a collaboration with Iridium, a satellite communications company, to bring two-way satellite communication to Android smartphones. This partnership was met with great anticipation, as it signaled the potential for Android to catch up with Apple in this area.
However, the partnership abruptly ended in September 2023, leaving Android users with renewed uncertainty. Qualcomm cited a lack of interest from smartphone manufacturers as a primary reason for the decision. Additionally, the technical challenges of implementing satellite connectivity and Qualcomm’s strategic shift towards 5G and 6G technologies likely played a role.

The Impact on Android Users
The demise of the Qualcomm-Iridium partnership has left Android users in a state of limbo. While there are other chipmakers, such as MediaTek, working on satellite connectivity solutions, it is unclear when these solutions will be available to Android consumers. Moreover, even if these solutions emerge, the high cost of implementing satellite connectivity may limit its availability to high-end Android devices.

The Benefits and Challenges of Satellite Connectivity
Despite the setbacks, satellite connectivity holds immense potential for Android devices. Its ability to provide emergency communication, global coverage, and secure communication for military and government applications makes it a valuable technology.
However, satellite connectivity is not without its challenges. The high cost of implementation, reliability issues in harsh weather conditions, and slower speeds compared to cellular networks and Wi-Fi are significant hurdles that need to be addressed.

The Road Ahead for Android Satellite Connectivity
The future of satellite connectivity for Android devices remains uncertain. While there are promising developments underway, it is likely that Android users will have to wait for some time before this technology becomes widely available and affordable.
In the meantime, Android users can still rely on cellular networks and Wi-Fi for connectivity in most areas. However, for those who venture into remote regions or experience connectivity disruptions, satellite connectivity offers a beacon of hope for staying connected in times of need.
Expanding on the Implications of Android’s Delayed Satellite Connectivity
The delayed arrival of satellite connectivity for Android devices has far-reaching implications that extend beyond mere inconvenience. It highlights the challenges of bringing cutting-edge technology to a diverse and ever-evolving mobile platform, and it underscores the importance of collaboration and innovation in this rapidly developing field.
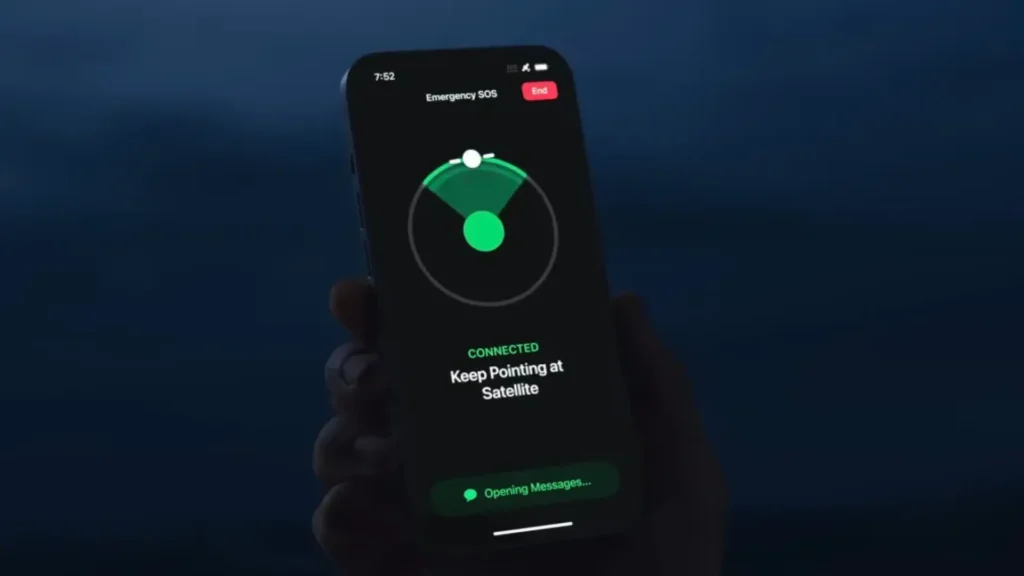
The Challenge of Fragmentation
Android’s open-source nature and vast ecosystem of device manufacturers have been both a blessing and a curse. While it has fueled the platform’s growth and adaptability, it has also created a fragmented landscape, making it more difficult for new technologies, such as satellite connectivity, to gain widespread adoption.
Smartphone manufacturers often prioritize their own proprietary features and software integrations, making them hesitant to adopt standardized solutions that may not align with their specific strategies. This fragmentation poses a significant obstacle for companies like Qualcomm and Iridium, which need broad support from device makers to bring their satellite connectivity solutions to market.
The Need for Collaboration and Innovation
Overcoming these challenges will require a concerted effort from various stakeholders within the Android ecosystem. Chipmakers, device manufacturers, software developers, and network providers must work together to establish industry-wide standards and ensure that satellite connectivity is seamlessly integrated into the Android experience.
This collaboration should be complemented by ongoing innovation to address the technical challenges of satellite connectivity. Reducing latency, improving data rates, and optimizing power consumption are crucial areas for improvement to make satellite connectivity a truly viable alternative to cellular networks and Wi-Fi.

The Potential Impact on Rural and Remote Communities
The delayed availability of satellite connectivity for Android devices has a disproportionate impact on rural and remote communities. These areas often lack reliable cellular coverage, leaving residents with limited access to communication and information services.
Satellite connectivity could bridge this digital divide, providing these communities with a lifeline for emergency communication, access to educational resources, and opportunities for economic development. The ability to connect with the outside world can be transformative for individuals and communities, fostering a sense of inclusion and enabling them to participate more fully in the digital age.
Conclusion
While users may have to wait longer than expected for satellite connectivity, the potential benefits of this technology are undeniable. Overcoming the challenges of fragmentation, fostering collaboration, and driving innovation are essential steps in bringing this technology to fruition. The positive impact on rural and remote communities further underscores the importance of bridging the digital divide and ensuring that everyone has access to the transformative power of connectivity.









